Our France flags are produced in the traditional 2:1 ratio used for National flags in the UK so this flag will match others of the same size if you are flying several flags together. We use a MOD grade Knitted Polyester which has been tested for its durability and suitability for production of flags.
Trivia
Technical Specifications
| Adopted |
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Proportion | 2:3 | |
| Design |
|

Brief History
The Kingdom of France existed ever since the division of West Frankia from the Carolingian Empire. Until then, neither Frankia nor the Empire had used anything that could truly be called a national flag. Even in the Anciens Regime of France, the idea of a national flag was fuzzy at best, and its closest equivalent would be the royal standard. The Royal Standard of France was a blue field, adorned with rows of fleur-de-lys devices. This came into use around the early 13th Century.
The flag would change under Charles V, simplified with only three fleur-de-lys devices. This was instituted upon the reconquering of French territories, which had been lost to England. It was such a significant return to form for the nation that the term ‘France Moderne’ came into parlance. Another flag that began to represent France at this time was the white cross. Usually it was set on a blue field, but this could be exchanged for regimental colours.
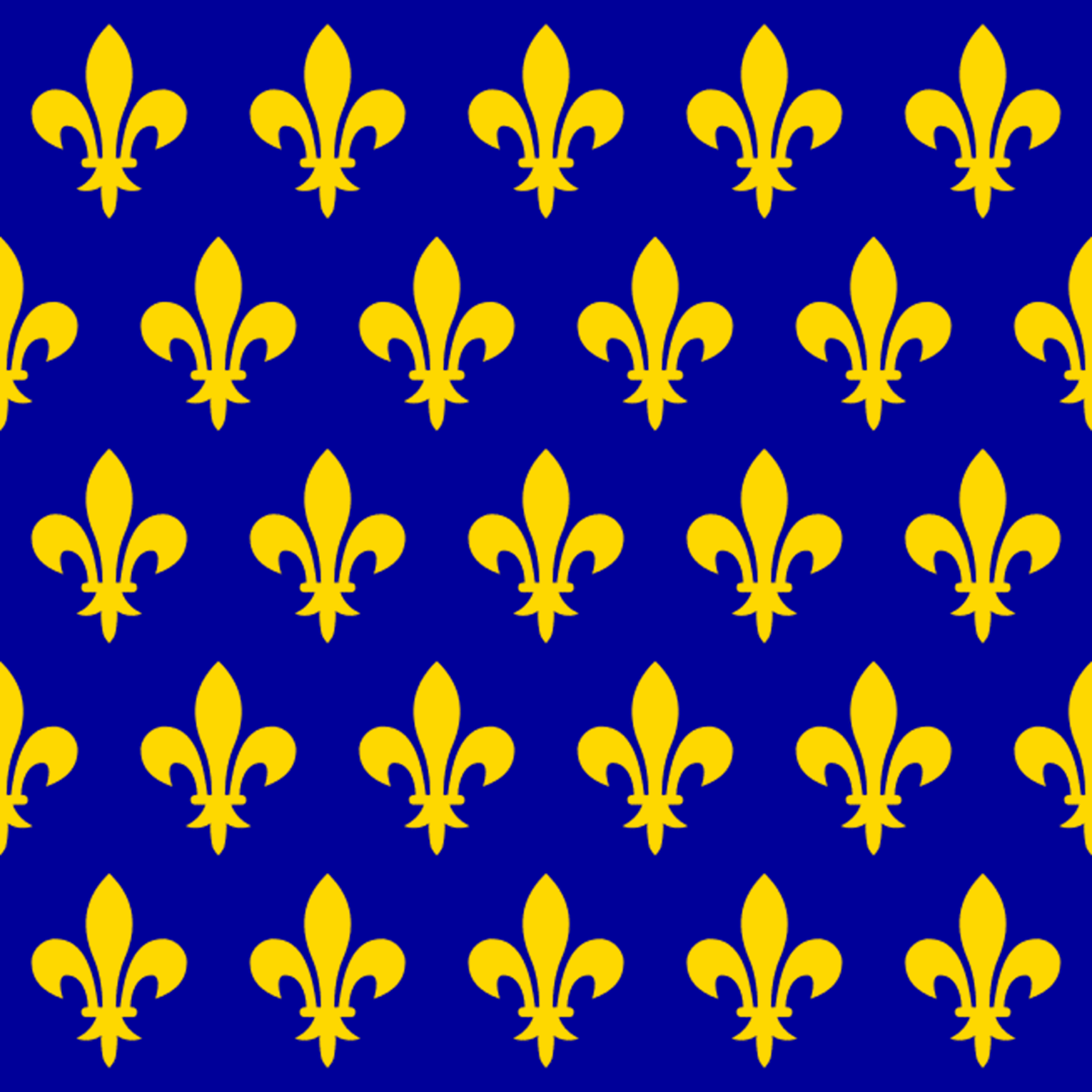

Flag of France (12th -14th Century)

Flag of ‘France Moderne’ (1376 – 1589)
The French Wars of Religion ended the Valois dynasty, and the next King of France, Henry IV, hailed from the House of Bourbon. A new royal standard brought back the wallpaper-like tiled fleur-de-lis, but on a white field.
A new, undecorated military ensign was also introduced. For the next two centuries, the French persistently waged war under a formidable, deadly white flag.
The French Revolution ended centuries of monarchal rule, and a new national flag was created, a tricolour of blue, white and red, said to symbolise the three ideals of the revolution: liberty, egality, and fraternity. There was a brief return to Bourbon rule, with a plain white national flag, after Napoleon’s defeat. A second revolution brought the tricolour back, through the kingdoms, empires and republics of France that followed.
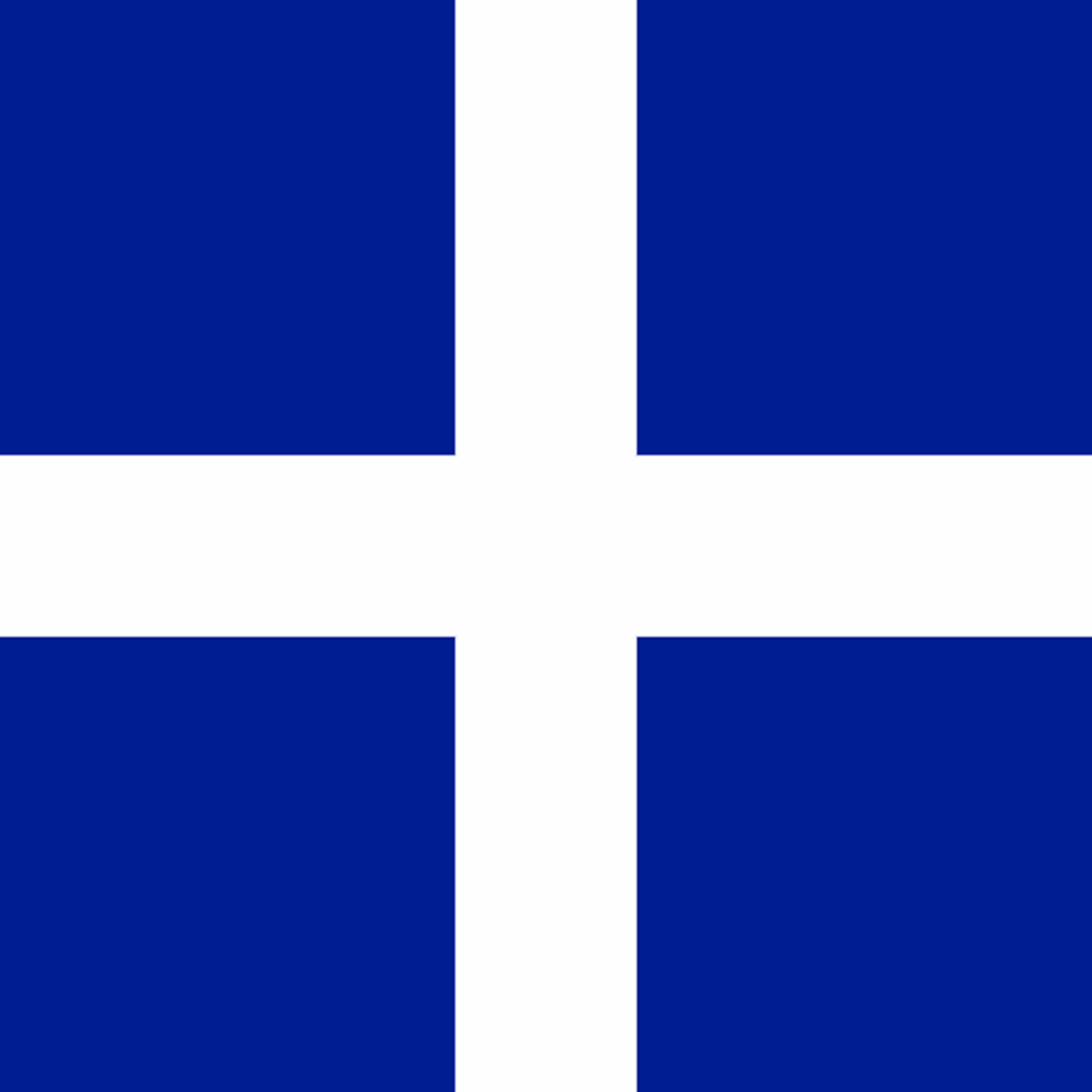

White Cross of France
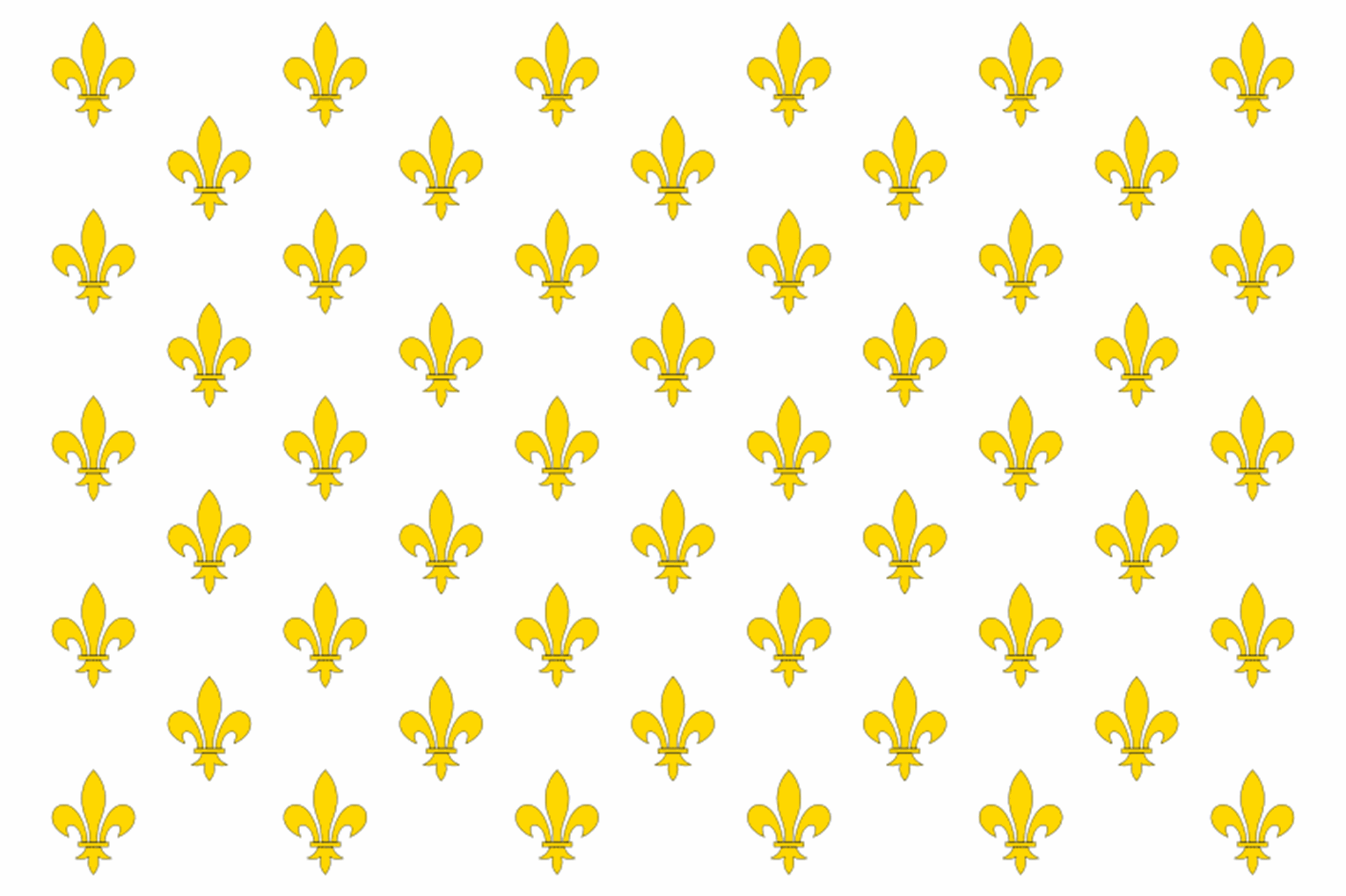
Flag of Bourbon–ruled France
During the Second World War, France was invaded by Nazi Germany. The French government was forced into exile, and surrender followed. French sovereignty now extended only to the south of France, while exercising limited jurisdictional authority in the north.
While the new Vichy government enthusiastically collaborated with Nazi oppression and genocide, French parliamentarian Charles de Gaulle escaped to England and created the government of Free France.
While the Free French had little control over the homeland, they coordinated the resistance movement and took control of the French colonies in Africa, before participating in D-Day and liberating Paris. The Cross of Lorraine was key to the flag of Free France; it was supposed to counteract the ideological symbolism of the Nazi swastika.
The collapse of the Vichy regime and the expulsion of Nazi forces paved the way for Free France to form a provisional government, and the undecorated tricolour was readopted.
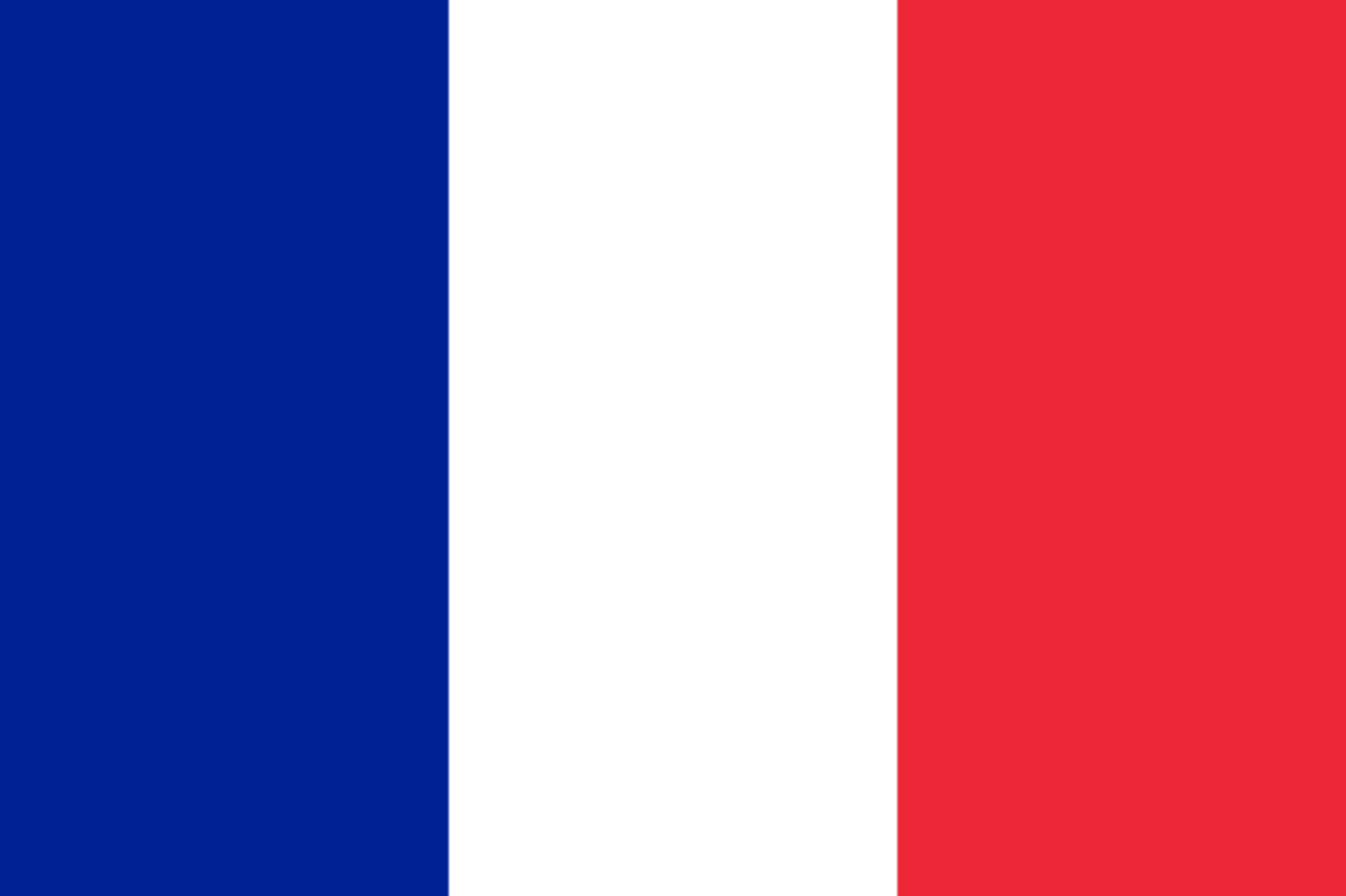
The Flag of the French Republic
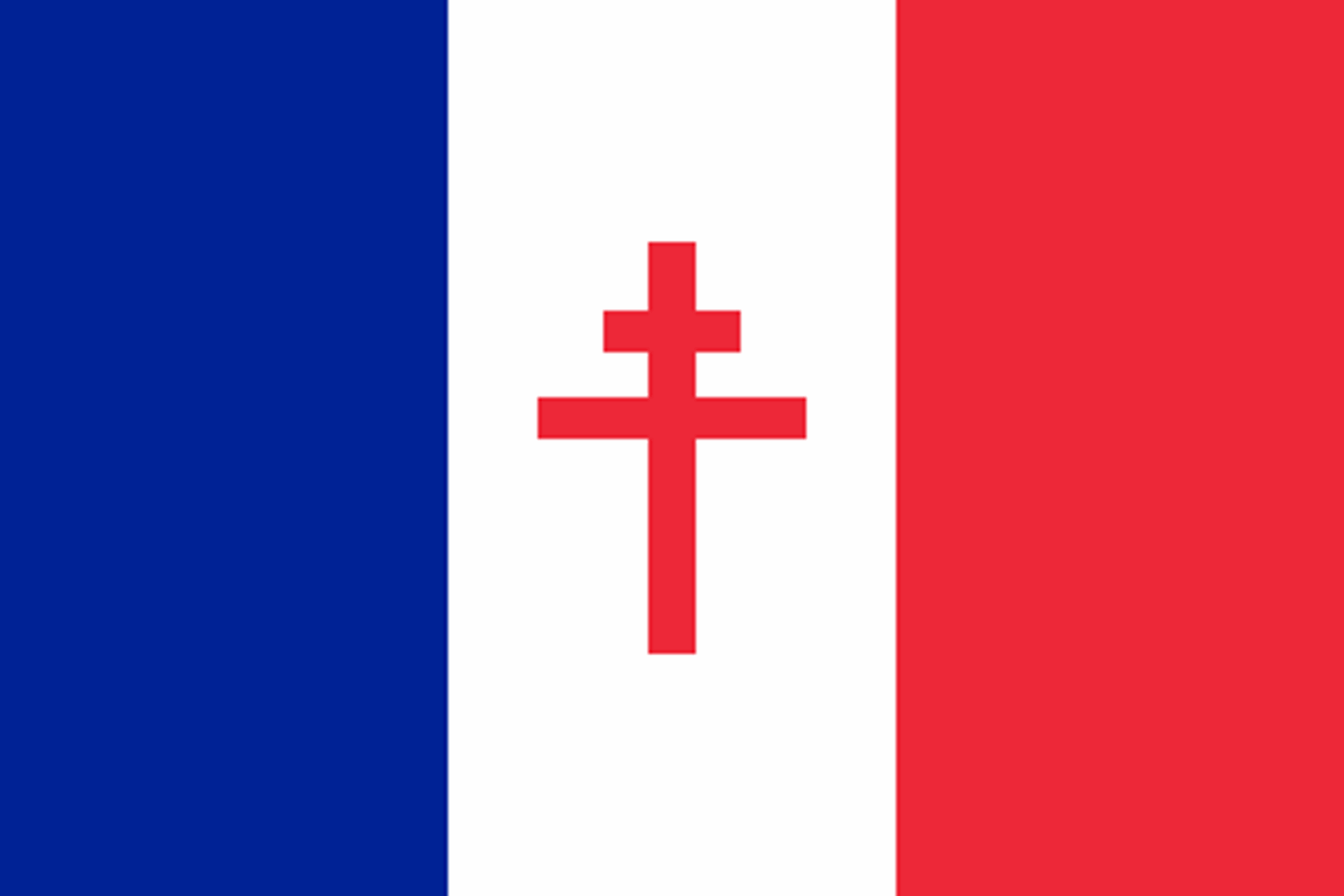
Flag of Free France
Other Flags of France
Although the national flag of France and the French ensign are very similar, they are not the same. The stripes of the flag are equal in size, but on the ensign, there is a width ratio of 30:33:37, with the red stripe as the largest. The historical naval jack of Free France is still flown on ships bearing the same name as their Free French wartime predecessors.
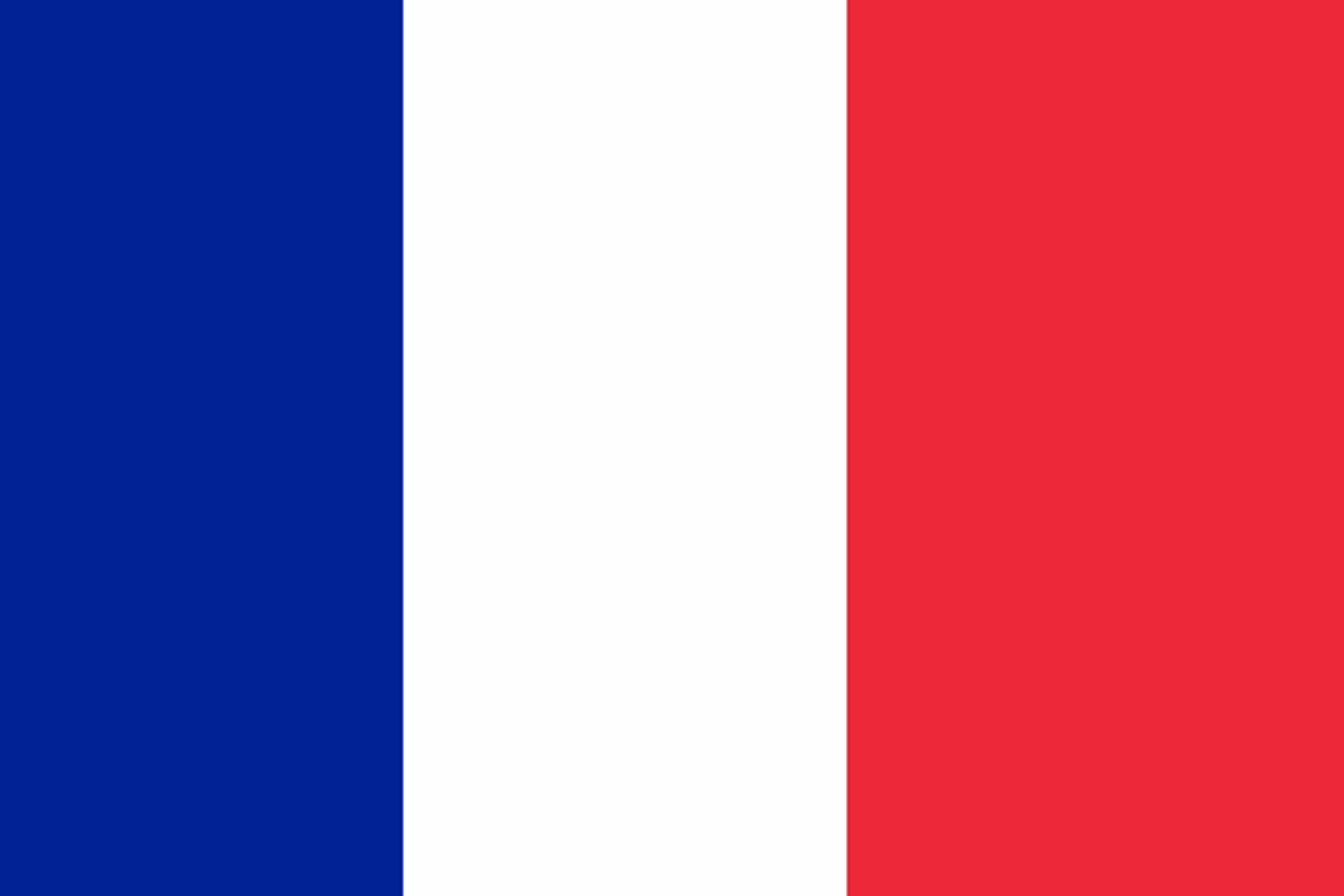
The Ensign of France

The Navel Honour Jack of Free France
Fleur-de-lis
The fleur-de-lis was the symbol of France from the 12th century up until the current French flag was created. The English translation of Fleur-de-lis is “lily flower” and is still being used on flags of current and former French colonies like Martinique and Quebec, Canada.

The Flag of Quebec

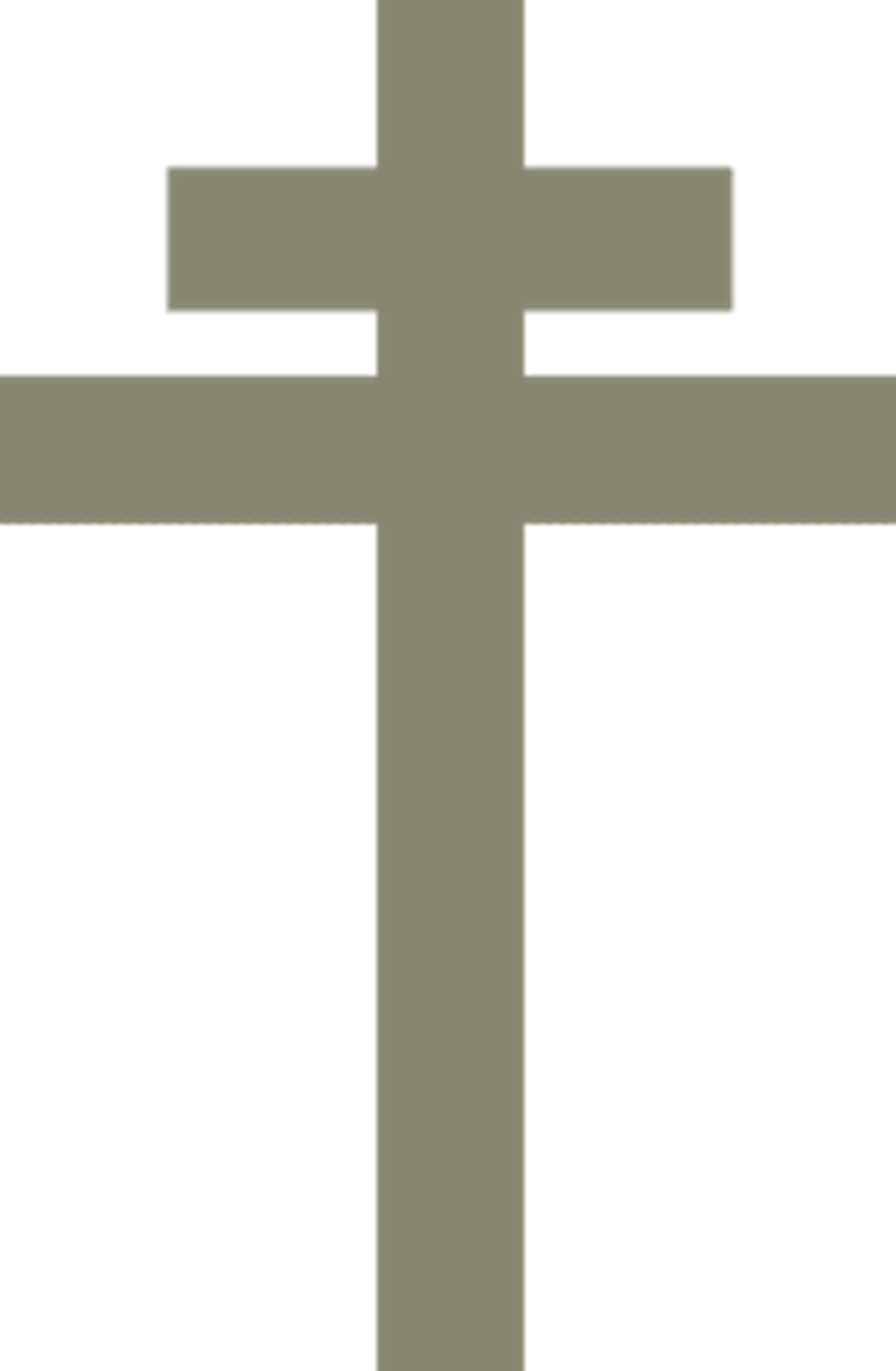
Cross of Lorraine
The Cross of Lorraine is a symbol of French patriotism. It is part of the heraldic arms of Lorraine in eastern France and served a symbol of French ambitions to recover it’s lost provinces when the northern third of Lorraine was annexed by Germany in 1871, 1918, 1940 and 1944.
It was also seen as the symbol of the Free French Forces led by Charles de Gaulle as an answer to the Nazi Swastika
Useful Links
Download Our Brochure
Download our electronic brochure to check out the full range of products we can supply you with.
Download NowContact Us
See a flag you like? We can manufacture any flag design in any size, speak to one of our experts to find out more.
Contact Us




